Energy & Environmental Science publication on minimization of CO2 emissions from the steel industry with electricity: a quantitative assessment
(13-07-2020)
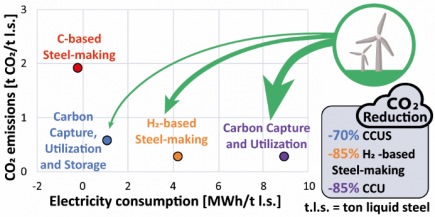
Marian Flores-Granobles and Mark Saeys addressed the steel industry’s decarbonization debate in a paper just published in Energy & Environmental Science. The steel industry uses carbon as reducing agent to remove oxygen from iron ore to produce hot metal in the blast furnace. Strategies to capture and store (CCS), utilize (CCU) or avoid CO2 emissions (H2-based) in steel production exist, but require vastly different amounts of renewable electricity. This study recommends the combination of CCS and CCU (CCUS) as the most efficient strategy, since the energy content of the blast furnace gas is used to produce value-added chemicals, thereby minimizing electricity requirements, while CO2 emissions are reduced with CCS.
Link: https://pubs.rsc.org/en/content/articlelanding/2020/ee/d0ee00787k#!divAb...
